On July 28, 2018, the 2018 International Statistical Conference (2018 JSM) was held in Vancouver, Canada. The Center for Statistics and Research of Tsinghua University sent a delegation to attend the conference and achieved fruitful results.
JSM is the largest academic activity in the international statistical community. It is an annual event for global statisticians. Thousands of experts, scholars and industry professionals from dozens of countries around the world participated in this event to discuss statistics. The latest scientific research results, breakthroughs and progress in applications, methods, and theories, as well as data science and other related issues. JSM has also established an open and shared platform for statisticians in the statistics and industry, enabling professionals to exchange ideas, establish mutually beneficial cooperation, and jointly promote the development of statistics.
Academic report
During the JSM conference, Professor Yu Sheng introduced Tsinghua Statistics to statistical scholars, experts and aspiring young people from all over the world. The center introduced the statistics discipline of Tsinghua University, which effectively enhanced the international recognition and academic influence of Tsinghua Statistics, and further promoted Tsinghua Statistics to the international platform.
 Professor Yu Sheng
Professor Yu Sheng
Academic Committee
On August 1st, local time, during the JSM annual meeting, the academic committee of the Center for Statistics Science of Tsinghua University met. The Academic Committee held discussions on the development of the central discipline during the JSM meeting each year. Several members were generally concerned about the current echelon construction, the training and promotion of young talents, and the positioning and development of the center. When it comes to the existing framework, we should actively promote open source projects and use the foundations and resources of the government and industry to help the center develop faster.
 Academic committee discussion
Academic committee discussion
 Academic committee member and center representative
Academic committee member and center representative
Discipline Development and Recruitment Presentation
On July 30th, local time, the Center for Statistics and Research of Tsinghua University successfully held the “Disciplinary Development and Recruitment Seminar” during the JSM meeting. This presentation aims to introduce in detail the development of the Statistics Department of Tsinghua University and the outstanding achievements of the Center for Statistics Research, and encourage high-level overseas statistical talents to join Tsinghua University to jointly promote the development of Tsinghua’s statistical discipline.
At the presentation, Prof. Yu Sheng from the center introduced the research, academic achievements and team composition of the center. Finally, Professor Niu Xiaoyue, the center’s visiting professor and deputy director of the Statistical Counseling Center, explained the positioning of Tsinghua University’s statistical consulting center and the rapid development in a short period of one year and the future development direction. The presentation attracted about 40 people from all walks of life and Tsinghua alumni, and achieved good publicity and expanded the industry’s influence and appeal.

 Tsinghua University JSM presentation meeting site
Tsinghua University JSM presentation meeting site
 Group photo of the delegation
Group photo of the delegation





 Examination and Presentation
Examination and Presentation
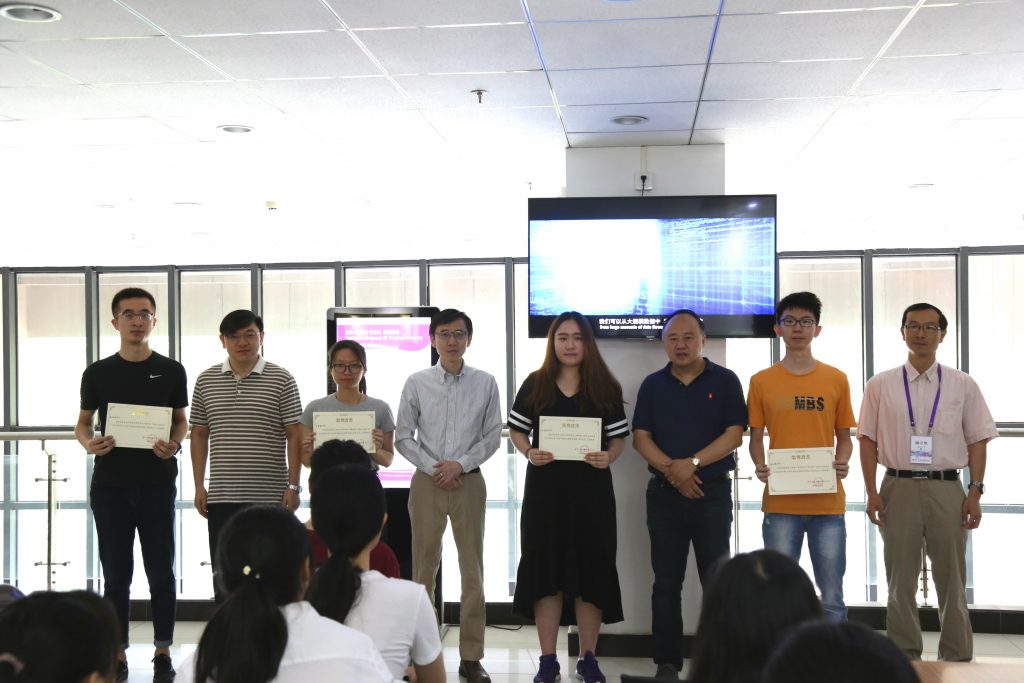
 The Award Ceremony
The Award Ceremony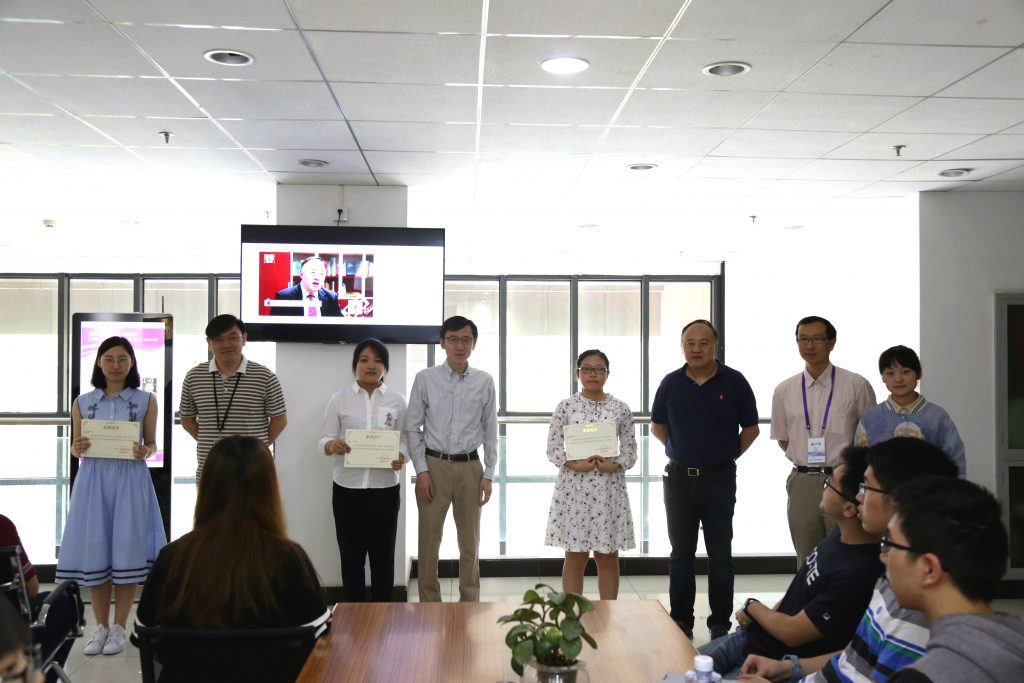





On June 4th, 2018. Prof. Suojin Wang from Texas A&M University visits the center and gives a talk titled“A simultaneous confidence band for the variance function of functional data”。




| CONFERENCE INFORMATION | ORGANIZERS | KEYNOTE SPEAKERS | PROGRAM | REGISTRATION | LOCAL INFORMATION | CONTACT US |
| KEY DATES | |
| May 20th, 2018 11:00 AM | Registration open |
| August 1st, 2018 10:00 AM | Payment open |
| September 1st, 2018 05:00 PM | Early registration deadline |
| September 30th, 2018 05:00 PM | Registration & Cancellation deadline |
With the rapid development of modern computing technology and the rise of the big data, opportunities and challenges in statistical computing have been witnessed in all dimensions of data science. Confronted to such condition, the Asian Regional Section of the International Association for Statistical Computing (IASC-ARS) and Chinese Association for Statistical Computing (IASC) jointly hold the IASC-ARS 25th Anniversary Conference & CASC 2nd Annual Conference in Beijing, China. The conference is dedicated to promoting further development of statistical computing in modern data science, and to providing a platform for international academic exchanges and cooperation among Statistical Computing and data science professionals.
Time:November 9 – 11, 2018
Venue: Beijing Conference Center, Beijing,China
(No. 88 Laiguangying West Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing)
The Asian Regional Section (ARS) of the International Association for Statistical Computing (IASC) is established by the Council in accordance with art. 12 of the IASC Statutes in 1993 by the name of the East Asian Regional Section (EARS) and the name is changed to the Asian Regional Section in 1998. It is composed of the members of the IASC residing in Asia. Our mission: to organize international or regional seminars, conferences, meetings. In particular, the ARS shall be responsible for arranging Asian meetings on computational statistics, which are abbreviated to IascAsian meetings hereafter; to promote research and training programs on theoretical and practical aspects of computational statistics; to foster evaluations of statistical computing techniques and programs; to publish scientific periodicals and books, reports and newsletters, independently or in cooperation with other organizations; to collaborate with other bodies having similar objectives.
The recent advancement of statistical research and increasing requirements arisen from the big data in various application fields have provided unprecedented challenges and opportunities in statistical computing. In order to respond to the pressing needs and seize the historical opportunity, a group of young statisticians, led by Professor Ke Deng of Center for Statistical Science at Tsinghua University, have jointly initiated the Chinese Association for Statistical Computing, as a branch of Chinese Association for Applied Statistics. The CASC was launched on March 19, 2017. The secretariat of CASC is located in the Center for Statistical Science at Tsinghua University.
CASC aims to unite the professionals in both academy and industry to enhance research and applications of statistical computing, towards boosting new theories and methodologies, promoting the applications in health, economics, industry, and other related fields, and advancing the development of statistics in China and overseas.
On May 16, 2014, the Center for Statistical Sciences of Tsinghua University (TCSS) was officially launched by the university council. The Center will foster and coordinate the development of statistical science in Tsinghua University. The goal is to build a powerful faculty team, to develop cutting-edge research, to strengthen collaborations between disciplines, and, in short, to establish a world-class center of excellence in statistics at Tsinghua University. The Center is an independent academic unit at the school level, while for administrative affairs it is affiliated to the Department of Industrial Engineering.
The Center is dedicated to promoting research and teaching of statistics in Tsinghua. Research areas include mathematical statistics, computational statistics, biostatistics, with emphasis on interdisciplinary studies, especially between statistics and life sciences, medicine, engineering, and business. With their recognized research excellence, engineering, business, and life sciences at Tsinghua University are well placed to benefit from as well as provide nourishment to statistical science. By integrating research resources across campus, The Center has set its goal on high impact academic achievements in both theoretical and applied statistics.
Coming soon…
Coming soon…
Early Registration: Before September 1, 2018
Regular Registration: September 1-30, 2018
Registration deadline: September 30, 2018
| Early Registration | Regular Registration | |
| Regular | 960 RMB | 1200 RMB |
| Student | 600 RMB | 750 RMB |
Note: Luncheons and a banquet will be covered by the sponsor during the conference. All participants are responsible to their own accommodation and transportation.
Accommodation Fee
| Standard Room at Building 6# | Standard Room at Building 9# | |
| Price | 550 RMB | 650 RMB |
Your room contains a piece of breakfast. The accommodation fee will be charged when you check in.
Step 1: Please fill the registration information.
Step 2: Please click the link to charge the registration fee.
Oops! We could not locate your form.
Please send an email to qianbao@mail.tsinghua.edu.cn before Oct. 1st if your schedule is changed.
Oops! We could not locate your form.
(2)Payment:
E-currency payment: Master, Visa
Secretariart for Chinese Association for Statistical Computing
Address: Weiqing Building 212, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China
Tel: +86 (10)-62786091
Fax:+86 (10) -62783842
Email:stats@tsinghua.edu.cn
Address: No. 88 Laiguangying West Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing
Tel: 86(10)-84901668
http://www.beijinghuiyizhongxin.com/encontact/176.html
Local transportation from the airport to the conference center
Address: No. 88 Laiguangying West Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing
Tel: 86(10)-84901668
http://www.beijinghuiyizhongxin.com/encontact/176.html


Tian’anmen (the Gate of Heavenly Peace), is located in the center of Beijing. It was first built in 1417 and named Chengtianmen (the Gate of Heavenly Succession). At the end of the Ming Dynasty, it was seriously damaged by war. When it was rebuilt under the Qing in 1651, it was renamed Tian’anmen, and served as the main entrance to the Imperial City, the administrative and residential quarters for court officials and retainers. The southern sections of the Imperial City wall still stand on both sides of the Gate. The tower at the top of the gate is nine-room wide and five –room deep. According to the Book of Changes, the two numbers nine and five, when combined, symbolize the supreme status of a sovereign. During the Ming and Qing dynasties, Tian’anmen was the place where state ceremonies took place. On October 1, 1949, chairman Mao Zedong proclaimed on Tian’anmen Rostrum the founding of the People’s Republic of China. Since then Tian’anmen has been the symbol of New China.
The Great Wall of China is a series of fortifications made of stone, brick, tamped earth, wood, and other materials, generally built along an east-to-west line across the historical northern borders of China to protect the Chinese states and empires against the raids and invasions of the various nomadic groups of the Eurasian Steppe. Several walls were being built as early as the 7th century BC; these, later joined together and made bigger and stronger, are collectively referred to as the Great Wall. Especially famous is the wall built in 220–206 BC by Qin Shi Huang, the first Emperor of China. Little of that wall remains. The Great Wall has been rebuilt, maintained, and enhanced over various dynasties; the majority of the existing wall is from the Ming Dynasty (1368–1644).
Apart from defense, other purposes of the Great Wall have included border controls, allowing the imposition of duties on goods transported along the Silk Road, regulation or encouragement of trade and the control of immigration and emigration.
The Great Wall stretches from Dandong in the east to Lop Lake in the west, along an arc that roughly delineates the southern edge of Inner Mongolia. A comprehensive archaeological survey, using advanced technologies, has concluded that the Ming walls measure 8,850 km (5,500 mi). This is made up of 6,259 km (3,889 mi) sections of actual wall, 359 km (223 mi) of trenches and 2,232 km (1,387 mi) of natural defensive barriers such as hills and rivers. Another archaeological survey found that the entire wall with all of its branches measures out to be 21,196 km (13,171 mi). Today, the Great Wall is generally recognized as one of the most impressive architectural feats in history.
The Temple of Heaven (Chinese: 天坛; pinyin: Tiantan) is an imperial complex of religious buildings situated in the southeastern part of central Beijing. The complex was visited by the Emperors of the Ming and Qing dynasties for annual ceremonies of prayer to Heaven for good harvest. It has been regarded as a Taoist temple, although Chinese heaven worship, especially by the reigning monarch of the day, predates Taoism.
In ancient China, the Emperor of China was regarded as the Son of Heaven, who administered earthly matters on behalf of, and representing, heavenly authority. To be seen to be showing respect to the source of his authority, in the form of sacrifices to heaven, was extremely important. The temple was built for these ceremonies, mostly comprising prayers for good harvests.
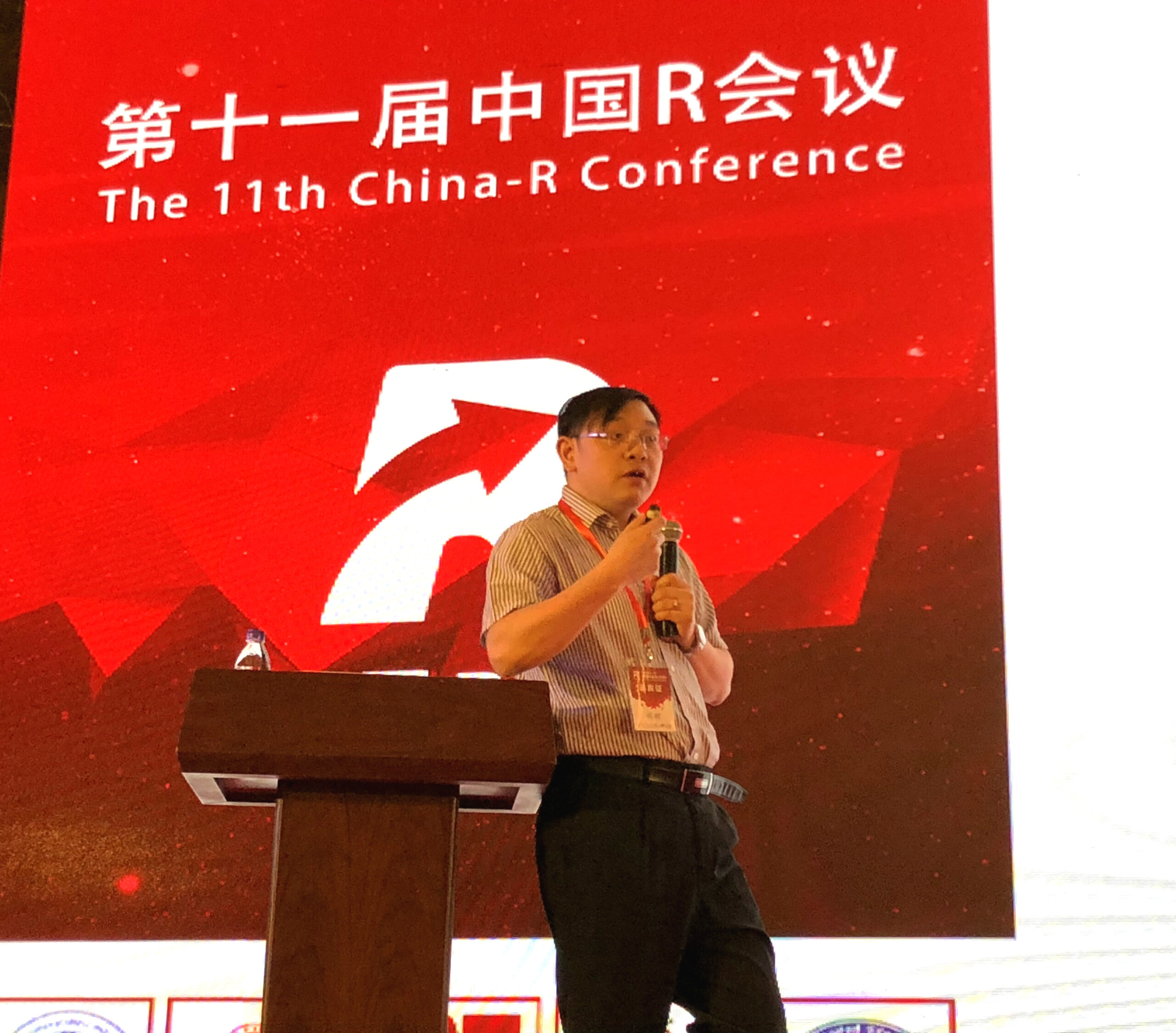





On May 25th, 2018, Prof. Ke Deng was Invited by The 11th China-R Conference and gave a talk titled “Statistics and the Health Industry in China.”